
Introduction
“Compliance is the cost of doing business. Non-compliance? That’s a whole different price tag.”
With UAE corporate tax now in full effect, businesses must navigate a 9% tax on profits over AED 375,000 while ensuring full compliance with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). Miss a deadline? That’s AED 10,000 in fines. Miscalculate your taxable income? Expect even steeper penalties.
If you’re running a business in the UAE, corporate tax is no longer optional, it’s mandatory. Whether you’re an SME, a free zone entity, or a multinational corporation, this guide will help you register, file, and stay compliant with keyword regulations while leveraging key exemptions and relief programs.
Understanding UAE Corporate Tax

Who Needs to Register for Corporate Tax?
If your business operates under a UAE trade license, you’re required to register. Here’s a breakdown of businesses that must comply with keyword:
- Mainland and free zone companies
- Foreign businesses with UAE-sourced income
- E-commerce and digital service providers selling to UAE customers
- SMEs and startups, even those earning below AED 3 million
- Freelancers and sole proprietors (if annual revenue exceeds AED 1 million)
👉 Important: Even if your business is making a loss, you still need to register.
Which Businesses Are Exempt?
Not every company is subject to corporate tax. Exemptions apply to:
- Government entities and public benefit organizations
- Natural resource extraction businesses (already taxed at the emirate level)
- Foreign companies with no permanent UAE establishment
- Investment funds and pension schemes
💡 Tip: Even if your business qualifies for an exemption, you must still apply for corporate tax registration before securing exempt status.
How to Register for UAE Corporate Tax
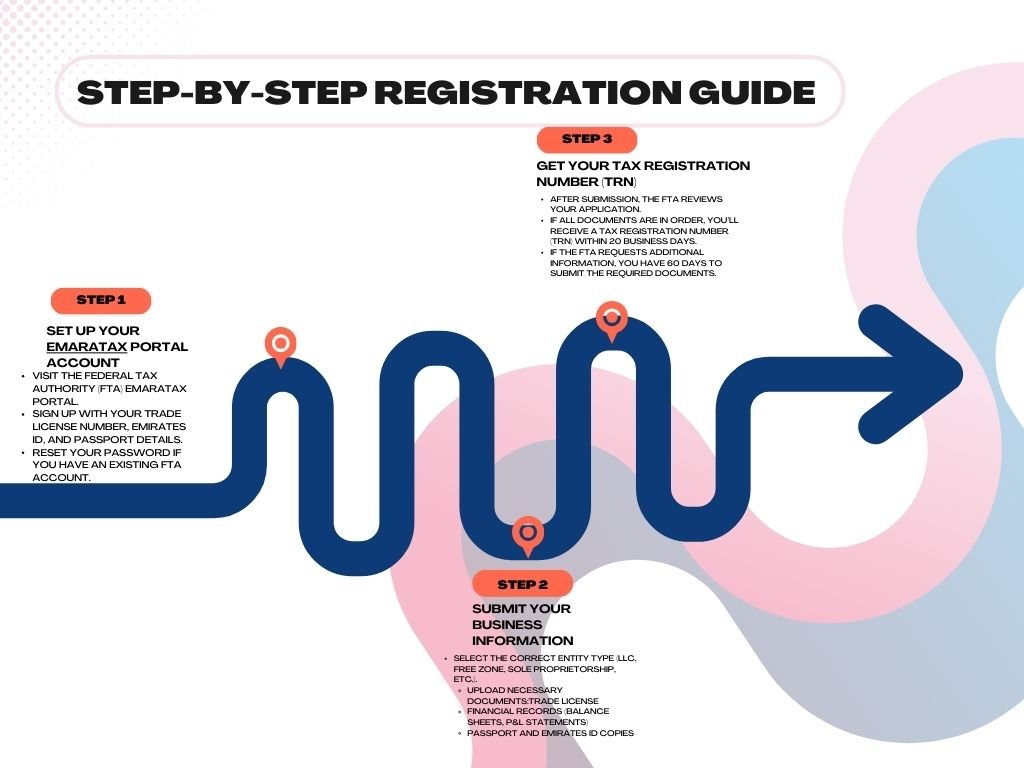
Step-by-Step Registration Guide
Step 1 – Set Up Your EmaraTax Portal Account
- Visit the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) Emara Tax portal.
- Sign up with your trade license number, Emirates ID, and passport details.
- Reset your password if you have an existing FTA account.
Step 2 – Submit Your Business Information
- Select the correct entity type (LLC, free zone, sole proprietorship, etc.).
- Upload necessary documents:
- Trade license
- Financial records (balance sheets, P&L statements)
- Passport and Emirates ID copies
Step 3 – Get Your Tax Registration Number (TRN)
- After submission, the FTA reviews your application.
- If all documents are in order, you’ll receive a Tax Registration Number (TRN) within 20 business days.
- If the FTA requests additional information, you have 60 days to submit the required documents.
✅ Pro tip: If you operate under multiple trade licenses, your registration deadline is based on the earliest-issued license not the most recent one.
Corporate Tax Filing & Compliance

Deadlines & Penalties: What You Need to Know
Missing a filing deadline isn’t just an inconvenience, it’s expensive.
- Businesses must file their tax returns within 9 months of their financial year-end.
- Penalty for late registration: AED 10,000.
- Additional fines for late filing, incorrect information, or failure to keep records.
💡 Example: If your financial year ends in December 2024, your corporate tax filing deadline is September 2025.
Small Business Relief – Do You Qualify?
If your business earns less than AED 3 million, you can apply for Small Business Relief, which simplifies your corporate tax obligations.
- No corporate tax liability if annual revenue stays under AED 3 million.
- Must still register and submit tax returns to maintain compliance.
- Once revenue exceeds AED 3 million, relief is no longer available, even if your income drops below the threshold later.
✅ Bottom line: If you’re a small business, don’t skip registration even if you qualify for relief.
How UAE Corporate Tax Compares Globally
UAE’s 9% Tax Rate vs. Other Countries
The UAE remains one of the most tax-friendly business destinations worldwide:
- UAE corporate tax: 9%
- EU average corporate tax: 21.3%
- OECD countries average: 23.04%
- G7 countries: 26.7%
Even with the introduction of corporate tax, the UAE offers one of the lowest rates globally, making it an attractive hub for international businesses.
What UAE Corporate Tax Means for Foreign Investors
The UAE’s business-friendly tax regime continues to draw foreign investment. However, multinational corporations operating in the UAE should be aware of:
- OECD BEPS regulations, which impose a minimum 15% tax rate on large multinational enterprises.
- Free zone tax benefits, where qualifying businesses may still enjoy a 0% tax rate under specific conditions.
How OECD BEPS Affects UAE Corporate Tax
What is OECD BEPS?
The OECD BEPS (Base Erosion and Profit Shifting) regulations are global tax rules aimed at preventing multinational corporations from shifting profits to low-tax jurisdictions to avoid taxation.
Impact on UAE Corporate Tax
Even though UAE’s corporate tax rate is 9%, businesses operating internationally may still be subject to the OECD’s global minimum tax of 15% if they qualify under BEPS regulations.
Here’s what UAE-based businesses should know:
- Free zone companies must meet “Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP)” criteria to continue benefiting from a 0% tax rate.
- Multinational corporations may need to comply with minimum effective tax rates even in tax-friendly jurisdictions like the UAE.
- Foreign investors with operations in multiple countries must ensure they meet OECD’s tax transparency and reporting standards.
💡 Why This Matters: If your UAE-based company has international operations, you must stay compliant with OECD tax rules to avoid penalties.
Final Takeaways – Stay Compliant & Tax-Smart!
Navigating keyword doesn’t have to be complicated. Here’s what to remember:
- All UAE businesses must register for corporate tax—even loss-making ones.
- The standard tax rate is 9% for profits over AED 375,000.
- Certain exemptions apply, but you must register before claiming them.
- Filing deadlines are strict—late submissions come with hefty penalties.
- Small Business Relief is available but doesn’t exempt you from registering.
📢 Need help registering for corporate tax? Book a free consultation today! 🚀
FAQs on UAE Corporate Tax
1. Who needs to register for UAE Corporate Tax?
All businesses operating under a UAE trade license, including mainland, free zone, and foreign entities with UAE-sourced income, must register for UAE Corporate Tax. Even small businesses and loss-making companies are required to register.
2. What is the corporate tax rate in the UAE?
The standard UAE Corporate Tax rate is 9% on taxable profits exceeding AED 375,000. Profits below this threshold are taxed at 0%.
3. Are free zone businesses subject to corporate tax?
Yes, free zone companies must register, but they may qualify for a 0% corporate tax rate if they meet the criteria of a Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP).
4. What happens if I don’t register for corporate tax?
Failure to register by the deadline results in a fine of AED 10,000. Additional penalties apply for late filings, incorrect tax returns, or failure to maintain records.
5. Can small businesses apply for tax relief?
Yes! Businesses with revenue under AED 3 million may apply for Small Business Relief, which simplifies tax compliance. However, registration is still required.
6. How do I register for UAE Corporate Tax?
Businesses must register via the FTA’s EmaraTax portal by submitting their trade license, financial records, and ownership details. Once approved, they receive a Tax Registration Number (TRN).
7. What is the deadline for filing corporate tax returns?
Corporate tax returns must be filed within 9 months after the end of the financial year. Missing the deadline incurs penalties.
8. Can multiple trade licenses be registered under one corporate tax account?
Yes, if they belong to the same legal entity. The earliest-issued trade license determines the tax registration deadline.
9. Are freelancers and consultants subject to corporate tax?
Freelancers and sole proprietors earning over AED 1 million annually must register for UAE Corporate Tax and file tax returns.
10. How can I deregister for corporate tax if I close my business?
Businesses that cease operations or qualify for exemptions must submit a deregistration request via EmaraTax, clear outstanding tax liabilities, and maintain records for 7 years post-deregistration.
More resources:

